Introduction to DG Synchronising Panels
DG synchronizing panels are sophisticated control systems designed to automatically synchronize and parallel multiple diesel generators. This allows for a scalable and resilient power supply, where generators can be added or removed from the grid based on the load demand. The primary function of these panels is to ensure that the generators operate in harmony, sharing the load efficiently and maintaining stable voltage and frequency.
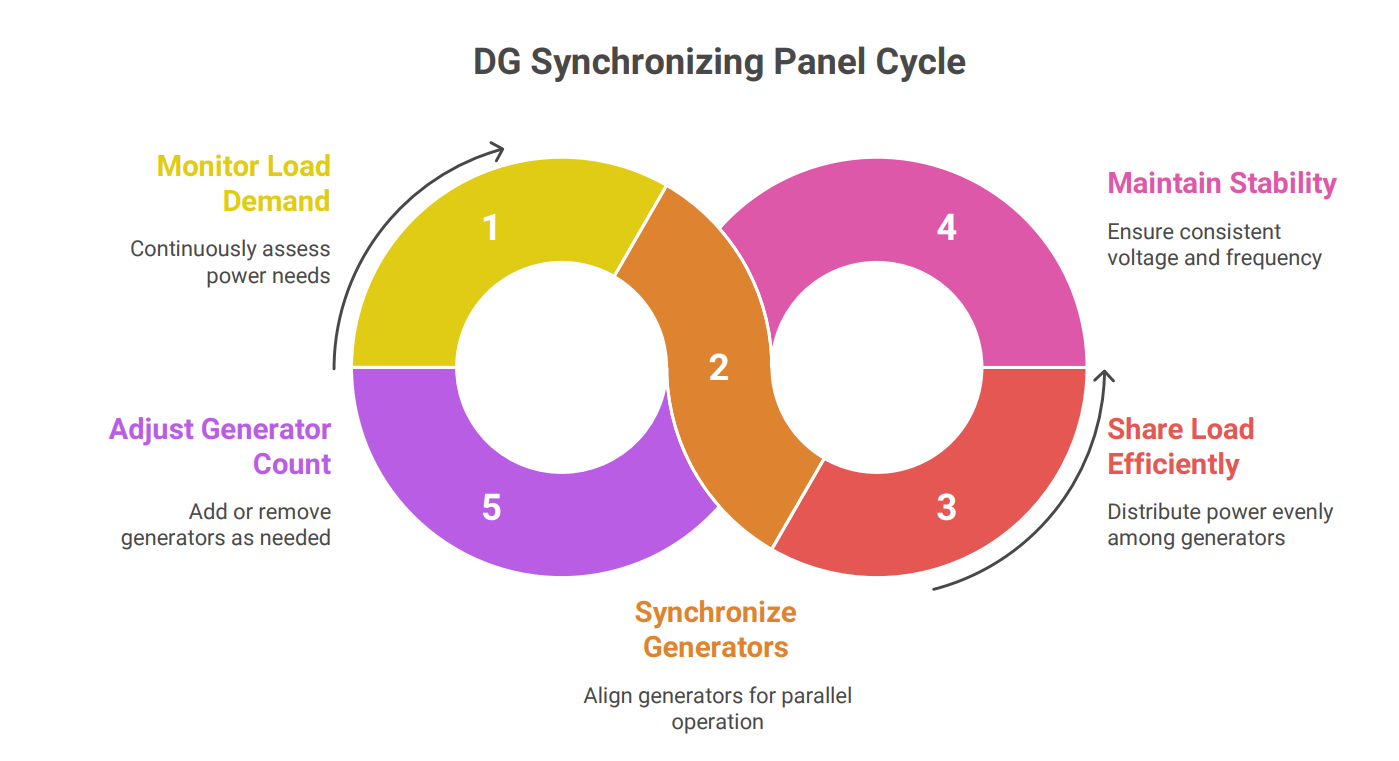
Purpose and Need for Synchronising Panels
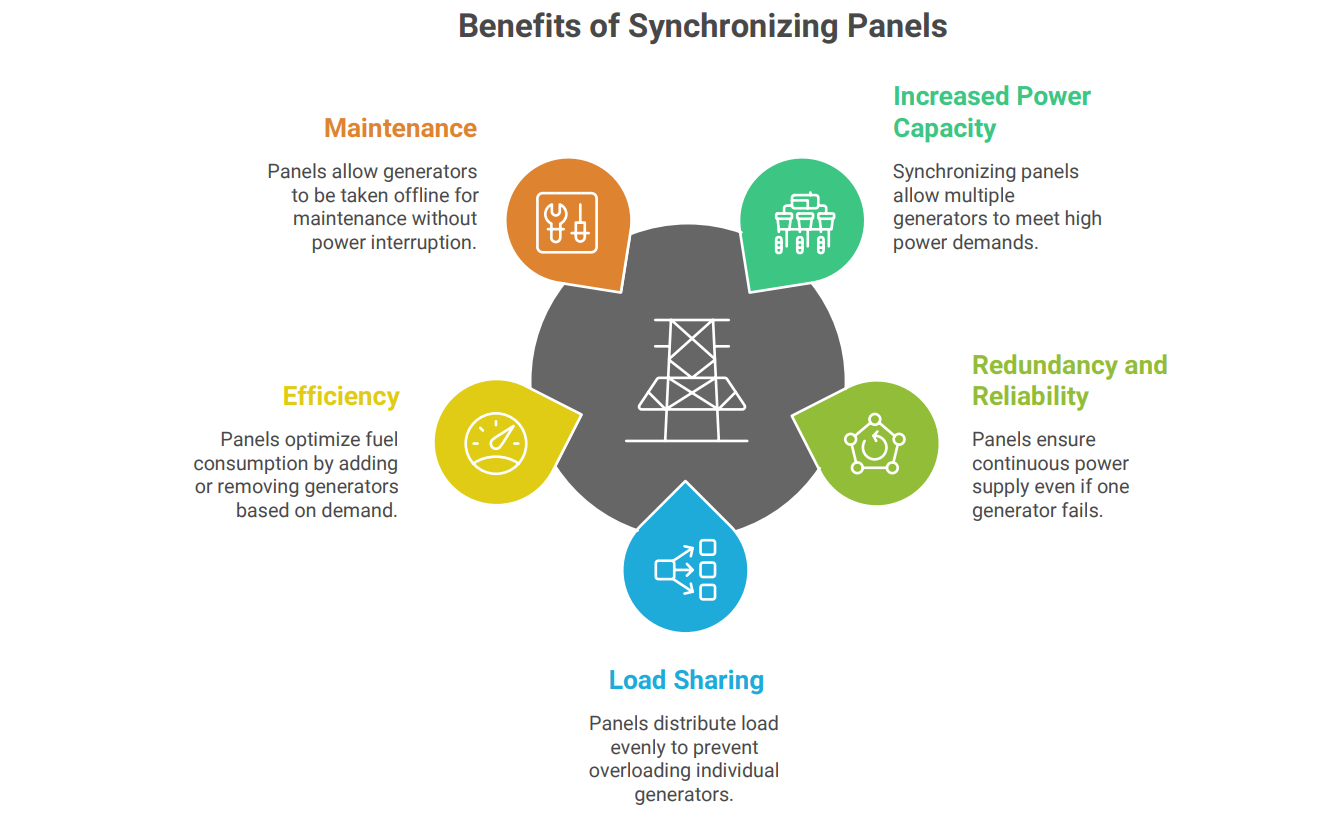
The need for synchronizing panels arises from several key requirements:
• Increased Power Capacity: When the power demand exceeds the capacity of a single generator, multiple generators can be synchronized to meet the load requirements.
• Redundancy and Reliability: In critical applications, synchronizing panels provide redundancy. If one generator fails, others can continue to supply power, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
• Load Sharing: Synchronizing panels ensure that the load is shared equally among the generators, preventing overloading of individual units and extending their lifespan.
• Efficiency: Generators can be added or removed from the grid based on the load demand, optimizing fuel consumption and reducing operating costs.
• Maintenance: Generators can be taken offline for maintenance without interrupting the power supply, as other generators continue to operate.
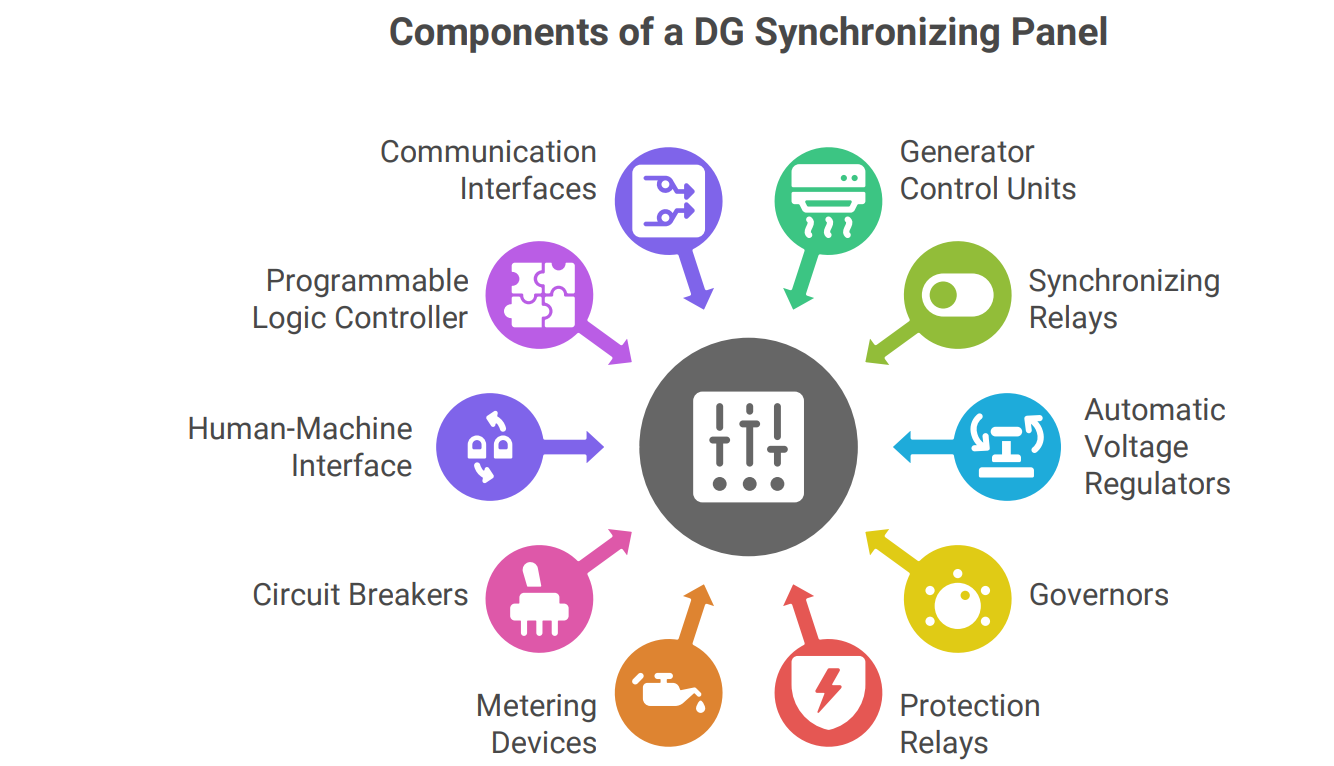
Components of a DG Synchronising Panel
A typical DG synchronizing panel consists of the following key components:
• Generator Control Units (GCUs): These units monitor and control the individual generators, including voltage, frequency, and load.
• Synchronising Relays: These relays compare the voltage, frequency, and phase angle of the incoming generator with the running generators or the grid.
• Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs): AVRs maintain a stable voltage output from each generator.
• Governors: Governors control the speed of the diesel engines, ensuring stable frequency.
• Protection Relays: These relays protect the generators and the system from faults such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and reverse power.
• Metering and Monitoring Devices: These devices display critical parameters such as voltage, current, frequency, power, and power factor.
• Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers are used to connect and disconnect generators from the grid.
• Human-Machine Interface (HMI): The HMI provides a user-friendly interface for monitoring and controlling the system.
• Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): The PLC acts as the central controller, coordinating the operation of all components.
• Communication Interfaces: These interfaces allow for remote monitoring and control of the system.
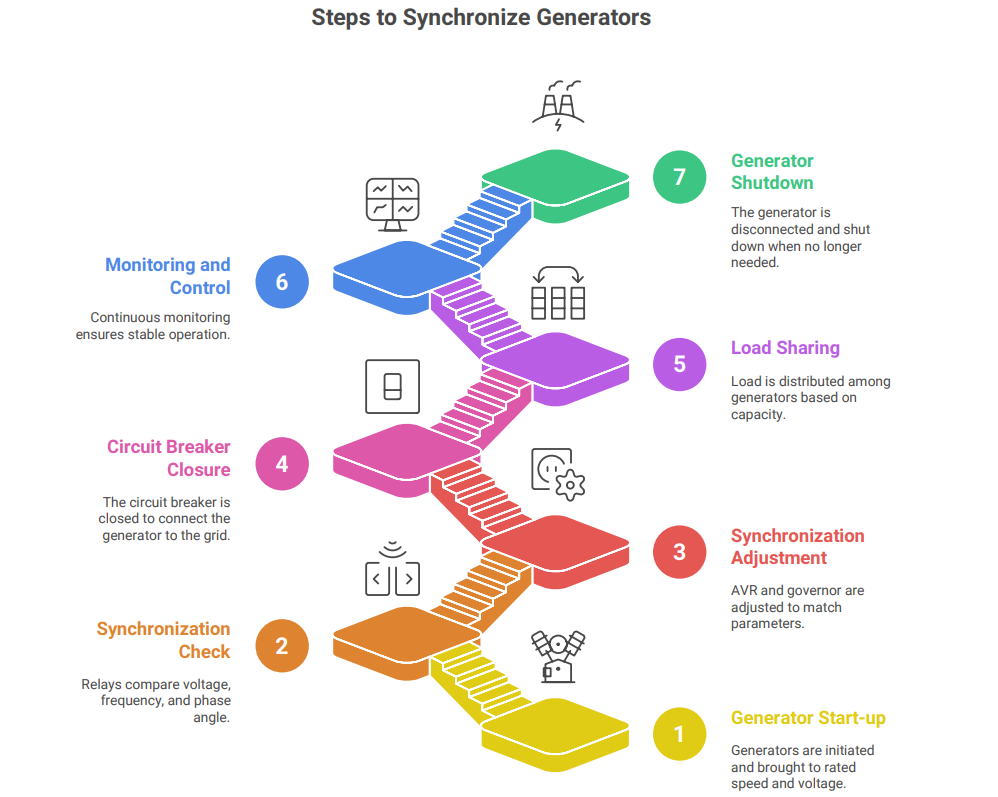
Operation of a DG Synchronising Panel
The operation of a DG synchronizing panel involves the following steps:
1. Generator Start-up: The generators are started and brought up to their rated speed
and voltage.
2. Synchronization Check: The synchronizing relays compare the voltage, frequency, and phase angle of the incoming generator with the running generators or the grid.
3. Synchronization Adjustment: The AVR and governor are adjusted to match the voltage, frequency, and phase angle of the incoming generator with the running generators or the grid.
4. Circuit Breaker Closure: Once the synchronization conditions are met, the circuit breaker of the incoming generator is closed, connecting it to the grid.
5. Load Sharing: The load is shared among the generators based on their capacity and settings.
6. Monitoring and Control: The system is continuously monitored and controlled to maintain stable voltage, frequency, and load sharing.
7. Generator Shutdown: When a generator is no longer needed, it is disconnected from the grid and shut down
Types of Synchronising Panels
Synchronising panels can be classified based on their level of automation and control:
• Manual Synchronising Panels: These panels require manual adjustment of voltage, frequency, and phase angle by an operator.
• Semi-Automatic Synchronising Panels: These panels automate some of the synchronization steps, such as voltage and frequency matching, but still require manual intervention for phase angle adjustment and breaker closure.
• Automatic Synchronising Panels: These panels fully automate the synchronization process, including voltage, frequency, and phase angle matching, as well as breaker closure.
Benefits of Using DG Synchronising Panels
The use of DG synchronizing panels offers several benefits:
• Increased Reliability: Redundancy ensures continuous power supply even if one generator fails.
• Improved Efficiency: Generators can be added or removed based on load demand, optimizing fuel consumption.
• Scalability: The system can be easily expanded to meet increasing power demands.
• Reduced Maintenance Costs: Generators can be taken offline for maintenance without interrupting the power supply.
• Enhanced Control: Precise control over voltage, frequency, and load sharing ensures stable and efficient operation.
• Remote Monitoring and Control: The system can be monitored and controlled remotely, improving operational efficiency
Applications of DG Synchronising Panels
DG synchronizing panels are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Hospitals: Ensuring uninterrupted power supply for critical medical equipment.
• Data Centers: Providing reliable power for servers and networking equipment.
• Manufacturing Plants: Maintaining continuous operation of production lines.
• Commercial Buildings: Supplying power for lighting, HVAC, and other essential systems.
• Power Plants: Supplementing grid power during peak demand or emergencies.
• Telecommunications: Ensuring continuous operation of communication networks.
• Oil and Gas Industry: Powering remote drilling and production sites
Considerations When Selecting a Synchronising Panel
When selecting a DG synchronizing panel, consider the following factors:
• Load Requirements: Determine the total power demand and the number of generators required.
• Level of Automation: Choose a panel with the appropriate level of automation based on operational needs and budget.
• Generator Compatibility: Ensure that the panel is compatible with the generators being used.
• Protection Features: Select a panel with comprehensive protection features to protect the generators and the system.
• Communication Capabilities: Choose a panel with the necessary communication interfaces for remote monitoring and control.
• Manufacturer Reputation: Select a panel from a reputable manufacturer with a proven track record.
• Service and Support: Ensure that the manufacturer provides adequate service and support
Conclusion
DG synchronizing panels are essential for providing reliable, efficient, and scalable power solutions. By understanding their purpose, components, operation, benefits, and applications, engineers, technicians, and other professionals can effectively utilize these panels to meet their power generation and distribution needs. Careful consideration of load requirements, automation levels, generator compatibility, and other factors will ensure the selection of the most appropriate synchronizing panel for a given application.
