Purpose of Low Voltage Distribution Boards
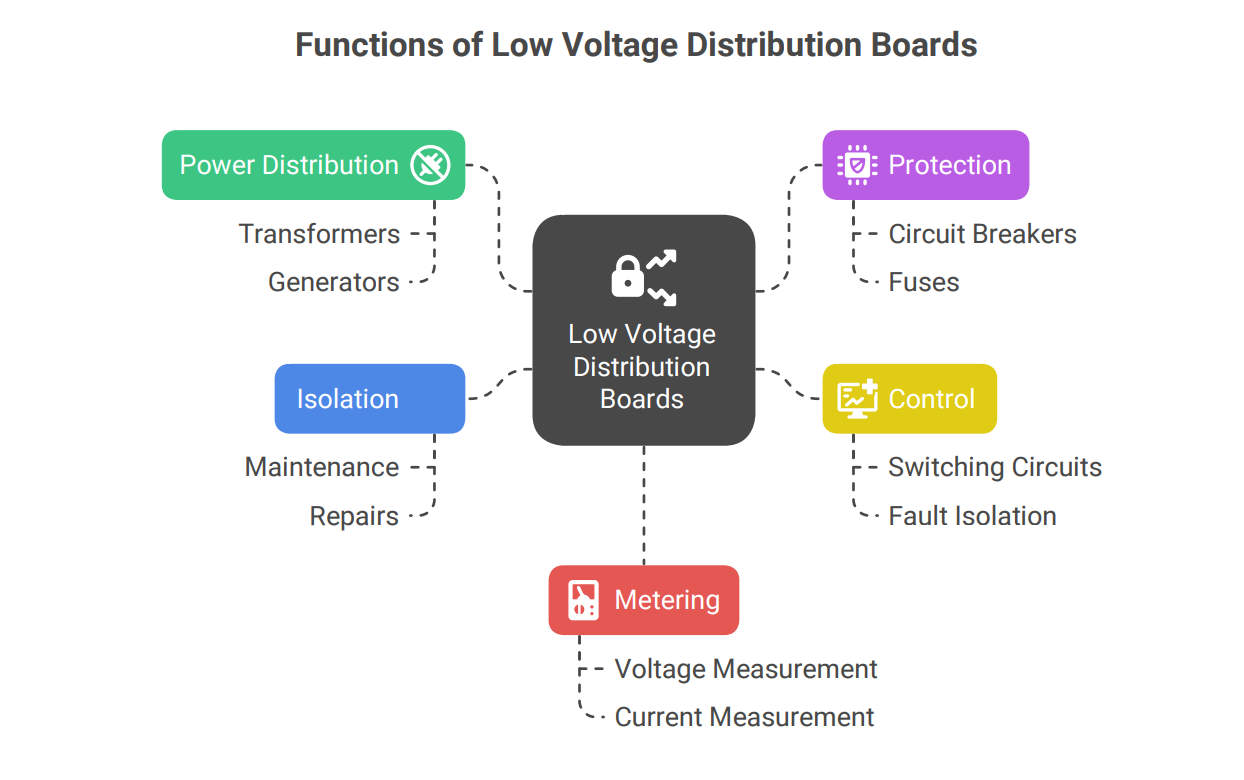
Low voltage distribution boards serve several essential functions within an electrical system:
• Power Distribution: They receive electrical power from a source, such as a transformer or generator, and distribute it to various circuits and loads throughout a facility.
• Protection: They incorporate protective devices like circuit breakers and fuses to safeguard circuits and equipment from overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults.
• Control: They provide a central point for controlling and monitoring the electrical system, allowing operators to switch circuits on or off, isolate faults, and monitor power consumption.
• Isolation: They enable the isolation of specific circuits for maintenance or repair purposes, ensuring the safety of personnel and preventing disruptions to other parts of the system.
• Metering: They often include metering devices to measure voltage, current, power, and energy consumption, providing valuable data for energy management and billing purposes.
Components of a Low Voltage Distribution Board
A typical LV distribution board consists of the following key components:
• Enclosure: The enclosure provides physical protection for the internal components and prevents accidental contact with live parts. It is typically made of steel or other durable materials and may be floor-standing or wall-mounted.
• Incoming Section: This section houses the incoming power supply connection, including the main circuit breaker or switch-fuse, which provides overall protection for the distribution board.
• Busbars: Busbars are conductive bars that distribute electrical power throughout the distribution board. They are typically made of copper or aluminum and are sized to handle the maximum current load.
• Outgoing Sections: These sections contain the outgoing circuit breakers or fuses that protect individual circuits and loads. Each outgoing section is connected to the busbars and provides a separate power supply for a specific load.
• Protective Devices: Circuit breakers and fuses are essential protective devices that interrupt the flow of current in the event of an overload or short circuit. Circuit breakers can be reset after a fault is cleared, while fuses must be replaced.
• Metering Devices: Voltmeters, ammeters, power meters, and energy meters provide real-time monitoring of electrical parameters, allowing operators to track power consumption and identify potential problems.
• Control Devices: Switches, pushbuttons, and indicator lights provide manual control and status indication for various circuits and functions.
• Wiring and Connections: High-quality wiring and connections are essential for ensuring reliable and safe operation. All connections must be properly tightened and insulated to prevent overheating and electrical faults.
Types of Low Voltage Distribution Boards
LV distribution boards are available in various types to suit different applications and requirements:
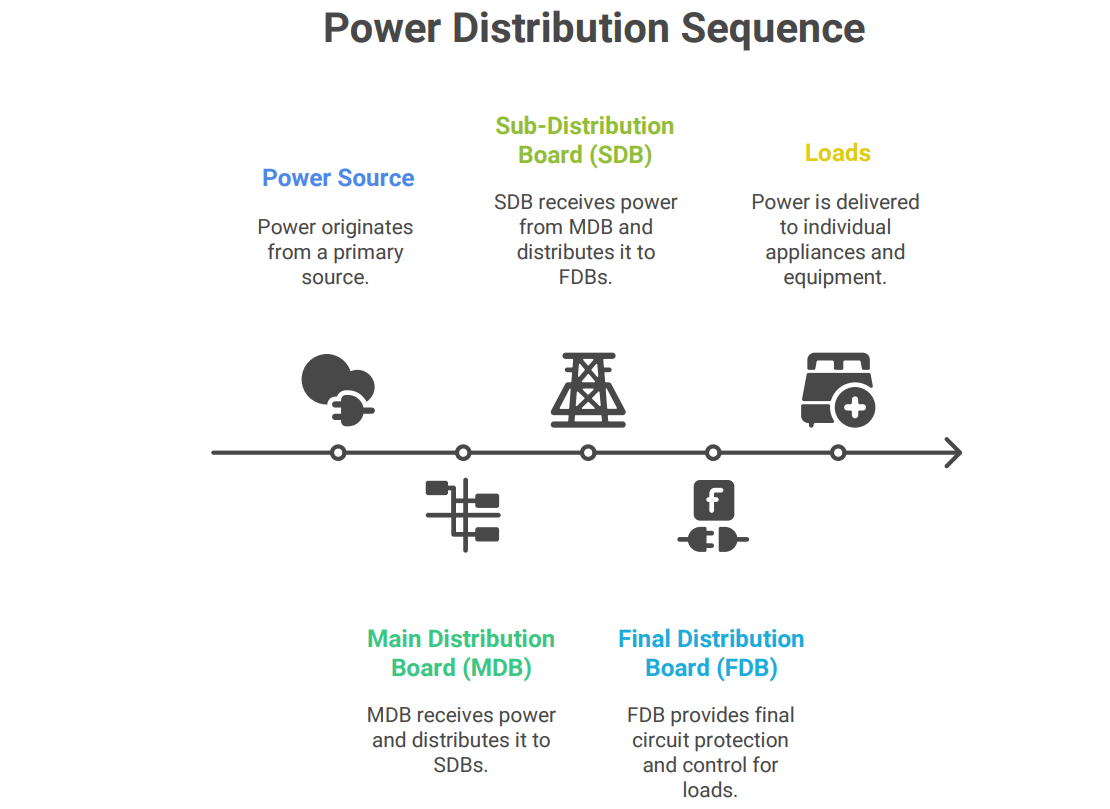
• Main Distribution Boards (MDBs): MDBs are the primary distribution points in a facility, receiving power directly from the source and distributing it to sub-distribution boards.
• Sub-Distribution Boards (SDBs): SDBs receive power from the MDB and distribute it to individual circuits and loads within a specific area or department.
• Final Distribution Boards (FDBs): FDBs are located closest to the loads and provide final circuit protection and control for individual appliances, lighting fixtures, and other equipment.
Selection Criteria for Low Voltage Distribution Boards
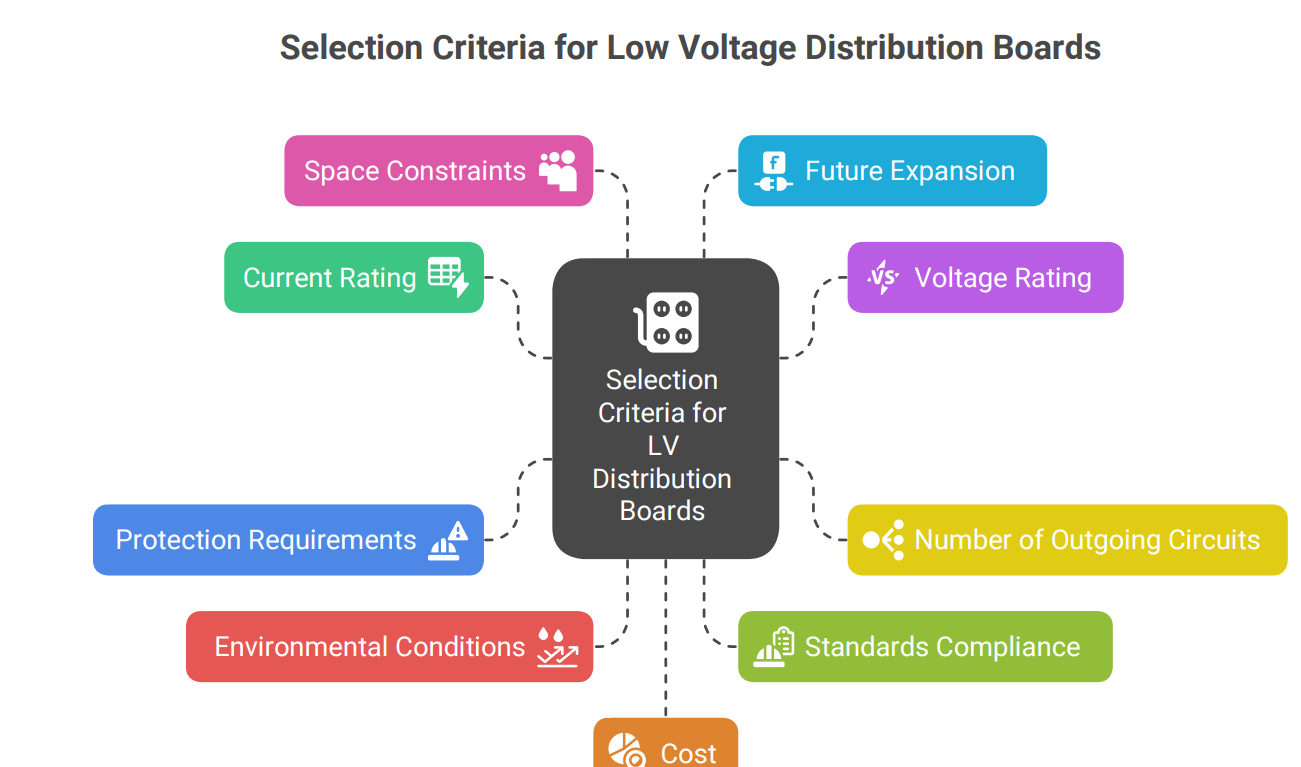
Selecting the appropriate LV distribution board for a specific application requires careful consideration of several factors:
• Current Rating: The distribution board must be able to handle the maximum current load of the connected circuits and equipment.
• Voltage Rating: The distribution board must be compatible with the voltage of the incoming power supply.
• Number of Outgoing Circuits: The distribution board must have enough outgoing circuits to accommodate all the connected loads.
• Protection Requirements: The distribution board must provide adequate protection against overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults.
• Environmental Conditions: The distribution board must be suitable for the environmental conditions in which it will be installed, such as temperature, humidity, and dust levels.
• Standards Compliance: The distribution board must comply with relevant industry standards and regulations, such as IEC 61439.
• Space Constraints: The size and configuration of the distribution board must be compatible with the available space.
• Future Expansion: The distribution board should have sufficient capacity for future expansion and additional circuits.
• Cost: The cost of the distribution board should be balanced against its features, performance, and reliability.
Standards for Low Voltage Distribution Boards
Several international and national standards govern the design, manufacture, and testing of LV distribution boards:
• IS 8623/ IEC 60439 /IEC 61439: This international standard specifies the design and testing requirements for low-voltage switchgear and control gear assemblies, including distribution boards.
Compliance with these standards ensures that the distribution board meets minimum safety and performance requirements.
Maintenance of Low Voltage Distribution Boards
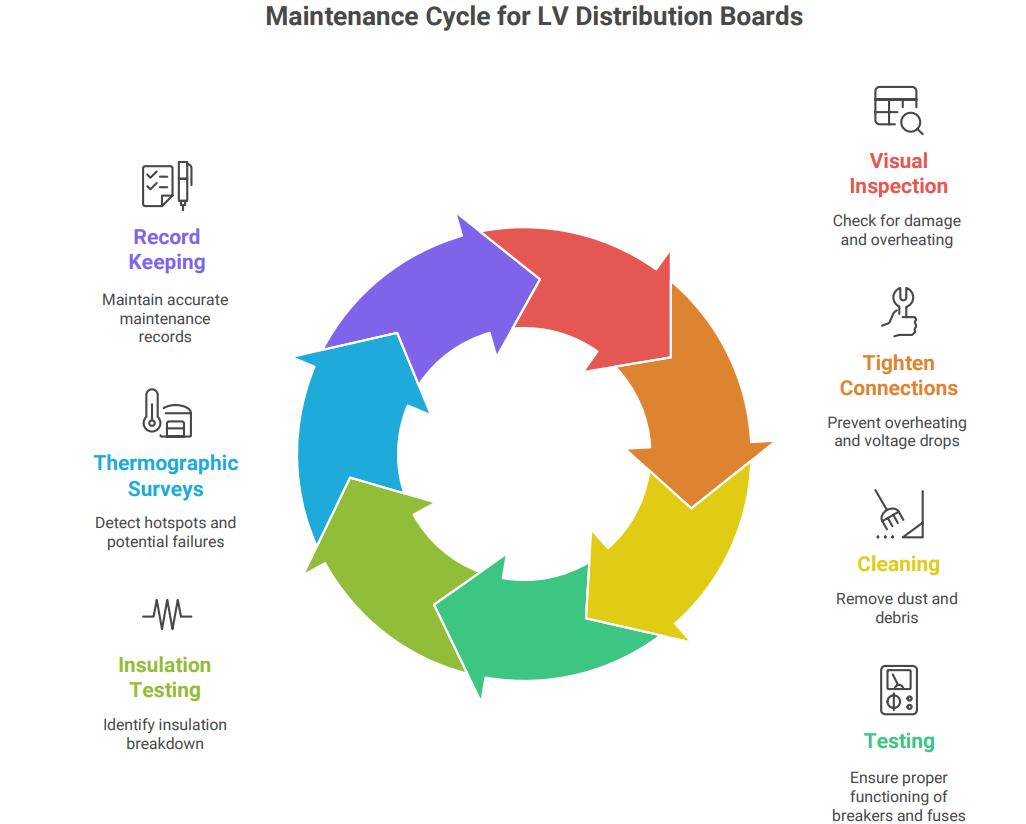
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the reliable and safe operation of LV distribution boards:
• Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the distribution board for signs of damage, overheating, or corrosion.
• Tightening Connections: Periodically tighten all electrical connections to prevent overheating and voltage drops.
• Cleaning: Clean the distribution board to remove dust and debris, which can contribute to overheating and insulation breakdown.
• Testing: Regularly test the circuit breakers and fuses to ensure they are functioning properly.
• Insulation Resistance Testing: Perform insulation resistance testing to identify any insulation breakdown or leakage currents.
• Thermographic Surveys: Conduct thermographic surveys to identify hotspots and potential problems before they lead to failures.
• Record Keeping: Maintain accurate records of all maintenance activities, test results, and repairs.
Safety Considerations
Working with LV distribution boards can be dangerous, and it is essential to follow proper safety procedures:
• Qualified Personnel: Only qualified and trained personnel should work on LV distribution boards.
• De-energization: Always de-energize the distribution board before performing any maintenance or repair work.
• Lockout/Tagout: Use lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental re-energization of the distribution board.
• Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, such as insulated gloves, safety glasses, and arc flash suits.
• Grounding: Ensure that the distribution board is properly grounded to prevent electric shock.
• Arc Flash Hazard: Be aware of the arc flash hazard and take appropriate precautions to minimize the risk of injury.
• Emergency Procedures: Know the emergency procedures in case of an electrical accident
By following these safety guidelines, you can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the safe operation of LV distribution boards.
